INNOVATIVE CASES
Read about innovative approaches being developed throughout Asia to address the challenges of aging, using new methods to keep seniors healthy and active and to provide care to those who need it.
Search for Innovative Cases
This database includes winners of the Healthy Aging Prize for Asian Innovation (HAPI), launched in 2020 to identify best practices throughout East Asia.
Category Type
Keywords
Countries
Type of Organization

Organization: ayumo Inc., Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka University Institute for Datability Science, National Hospital Organization Osaka-Minami Medical Center
LOCATION: Osaka, Japan
The concept of locomotive syndrome (LS) refers to reduced mobility due to impairment of the musculoskeletal system, which is a major contributor to the need for long-term care. A group of medical and technology researchers has developed a gait analysis device that uses AI to assess LS quickly and simply by just having older people walk a few meters in front of a camera.
KEYWORDS: Frailty, Preventive care

Organization: Rehab Home Ippo Co., Ltd.
LOCATION: Saitama, Japan
Rehab Home Ippo was established in 2011 as a small day care service for older people. Four years later, it combined that service with a small nursery school. That led to an important discovery: clients who, despite the staff’s best efforts, never smiled or engaged in activities suddenly lit up when they saw the children at the nursery. That realization triggered an innovative new approach to the company’s work: they
KEYWORDS: Caregiving, Dementia, Intergenerational
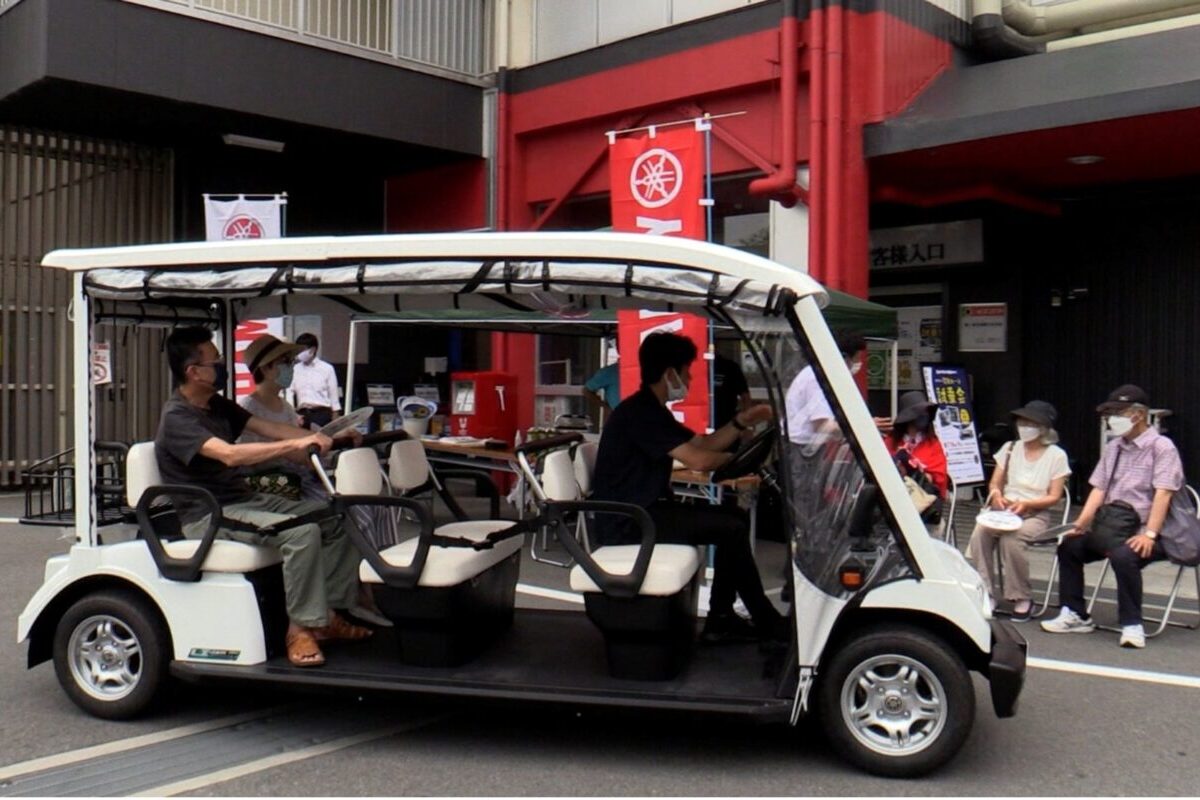

Organization: Center for Preventive Medicine, Chiba University, with Yamaha Motor Co. and Nihon Fukushi University
LOCATION: Chiba, Japan
Mobility is crucial for older adults to live healthy, active, and rewarding lives. Research institutes at Chiba University and Nihon Fukushi University worked with Yamaha Motor Co. and several local governments to address this problem by introducing electric carts that could be used on public roads in the community. They introduced an operational model that is easy for older people to use and easy for governments to implement.
KEYWORDS: Mobility, Social/community engagement

Organization: Osaka Kawasaki Rehabilitation University, Kaizuka City Health and Welfare Department Elderly Care Division, and Fuji Oil Corporation
LOCATION: Kaizuka City, Japan
Launched in 2017 as an industry-government-academia project, this initiative offers activities that contribute to the extension of healthy life expectancy among residents of Kaizuka City, focusing on health checks, exercise classes, and volunteer training projects.
KEYWORDS: Dementia, Frailty, Preventive care
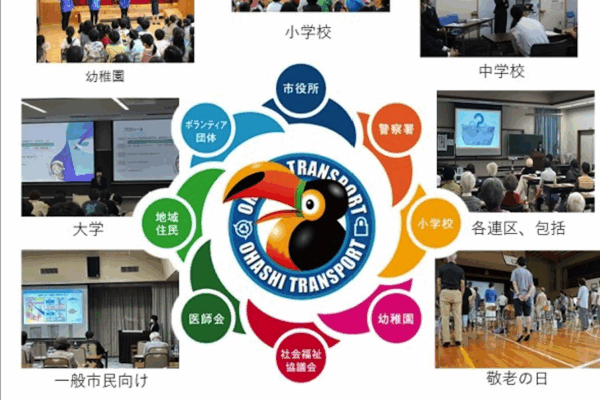
Organization: Ohashi Transport Co., Ltd., Seto Municipal Government, and the Seto City Social Welfare Council
LOCATION: Seto City, Japan
Ohashi Transport Co., a company with headquarters in Seto, had been carrying out in-house health management programs to maintain the mental and physical wellbeing of its employees as a means to improve each person’s vitality and productivity. They recognized that their experience could contribute to the promotion of health for their community, and so began working with the local government to implement a multi-pronged program focused on health education, exercise
KEYWORDS: Preventive care, Public awareness, Social/community engagement

Organization: Keio University, Shonan Fujisawa Campus (SFC), Takashi Iba Laboratory
LOCATION: Fujisawa, Japan
Keio University researchers developed a "thinking aid" for caregivers at eldercare facilities and at home to share better care practices. They developed a pattern language focused on the concept of mutual care, focusing on a relationship of "living together" rather than a relationship between "those who provide care and those who are cared for."
KEYWORDS: Caregiving
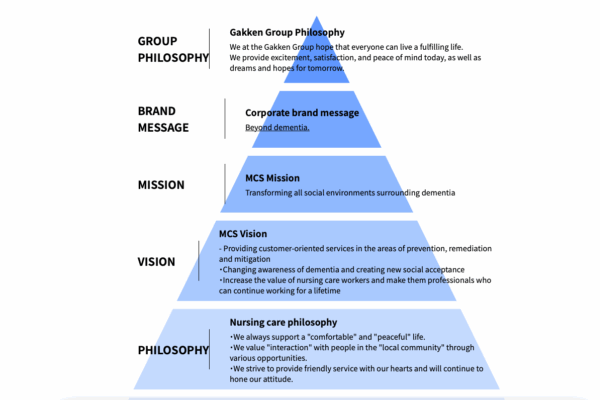
Organization: Medical Care Service (MCS) Co., Ltd.
LOCATION: Saitama, Japan
MCS operates hundreds of group homes and nursing homes in Japan and China. To improve their residents' quality of life, MCS established an evidence-based system that focuses on a secondary cause of dementia, the deterioration of physical activity, and primarily consists of medically based adjustments to areas such as hydration, nutrition, exercise, oral function, posture, mobility, and medication.
KEYWORDS: Caregiving, Dementia, Medical/health services

Organization: Mirai wo Tsukuru Kaigo Café
LOCATION: Tokyo, Japan
Kaigo Café is a professional, multidisciplinary, offline and online network that has been carrying out grassroots activities throughout Japan since 2012 that allow participants from all aspects of the medical and nursing care industry—regardless of their credentials or status—to talk freely and empower one another to continuously improve elder care.
KEYWORDS: Caregiving, Medical/health services

Organization: Tanotech Corporation
LOCATION: Hiratsuka City, Japan
TANO is a non-contact gamification system that promotes movement and social engagement for health promotion and rehabilitation for older people. It is being used in care facilities in Japan and overseas. The initiative seeks to connect education and welfare, promote society-wide cooperation through industry-government-academia partnerships, and create an environment in which children and students can develop an awareness of social issues from an early stage.
KEYWORDS: Caregiving, Frailty, Intergenerational, Medical/health services, Preventive care, Social/community engagement
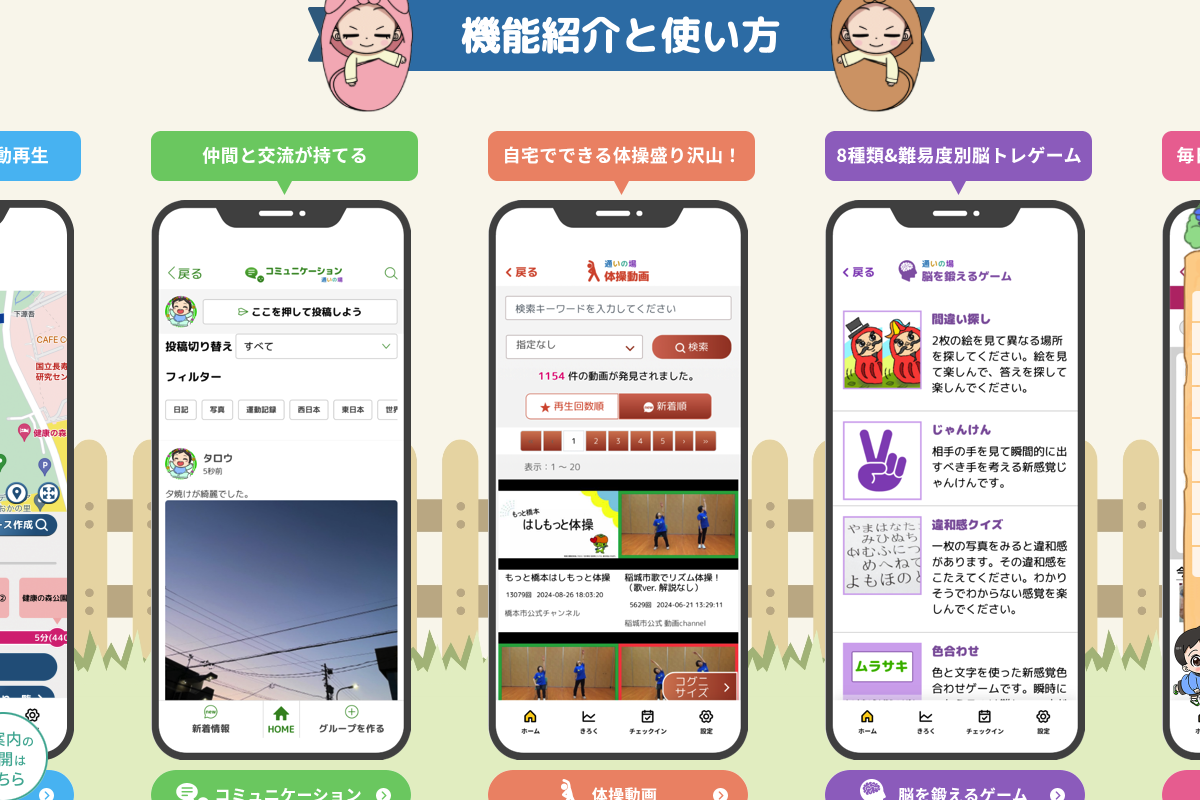
Organization: National Center for Geriatrics and Gerontology (NCGG)
LOCATION: Obu City, Japan
In response to COVID, a multidisciplinary team of physicians, therapists, and dieticians created an evidence-based Home Exercise Program for Older People (HEPOP), which was published one month later as a booklet and online, offering a menu of exercises and activities that can be easily practiced at home. It was integrated into the Ministry of Health's Online Kayoinoba (gathering place) app.
KEYWORDS: Frailty, Medical/health services, Preventive care

